Intelligent, guided autonomous materials research requires the ability to measure the microstructural properties of specimens and make correlations with mechanical properties and behavior. High-throughput microstructural characterization of structural materials is a challenge, however, because electron-based techniques such as SEM and EBSD require careful surface preparation and only examine the near-surface region.
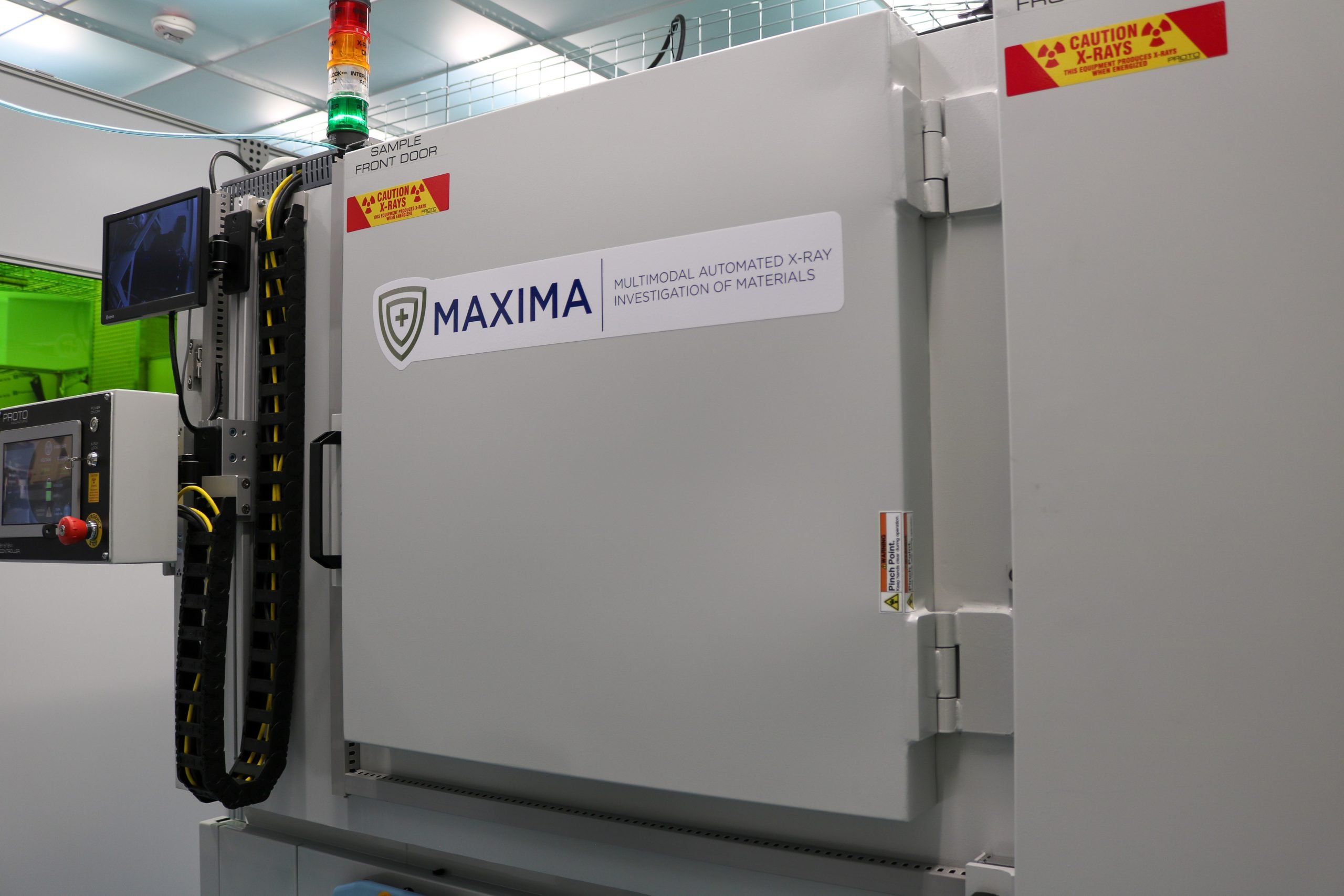
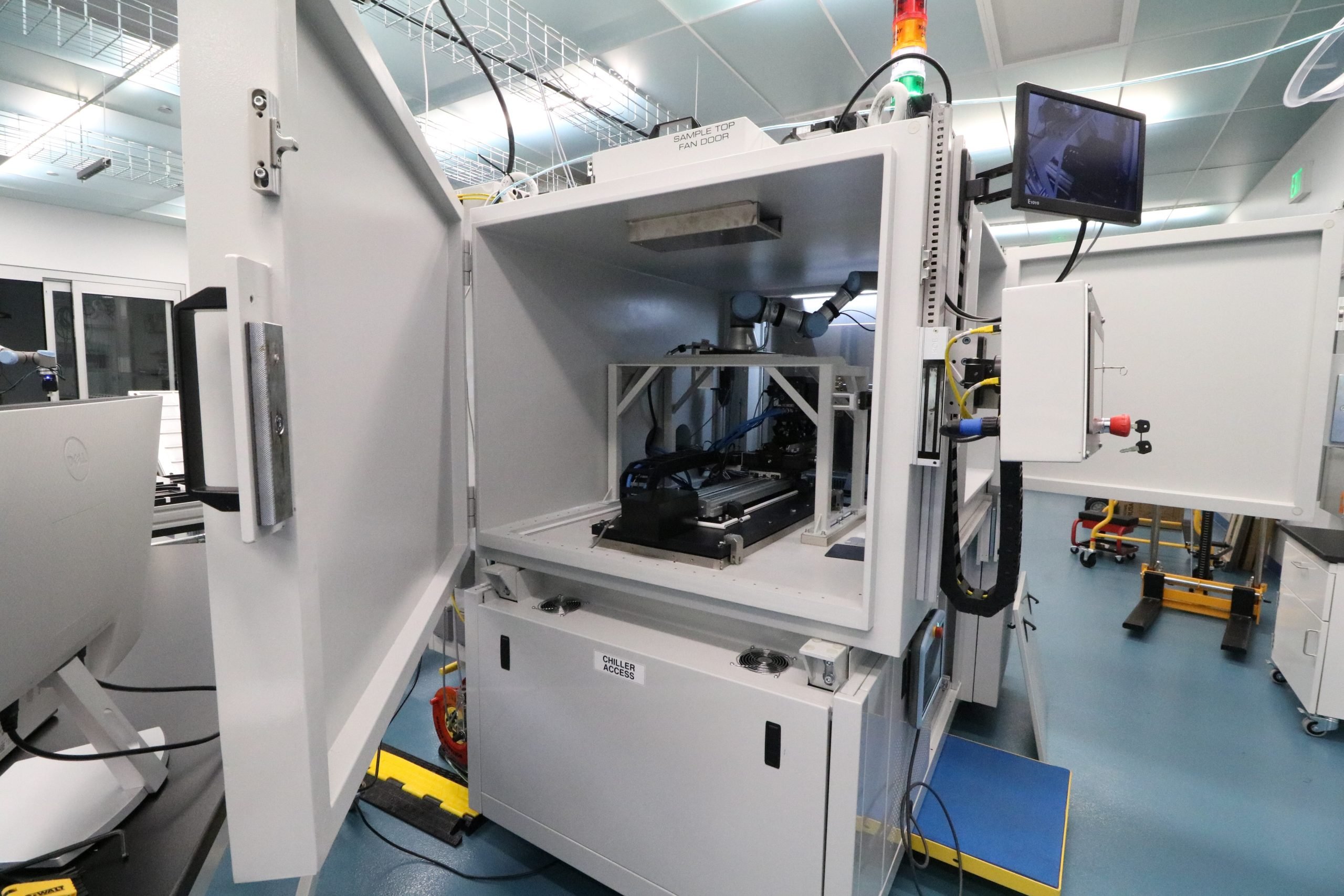
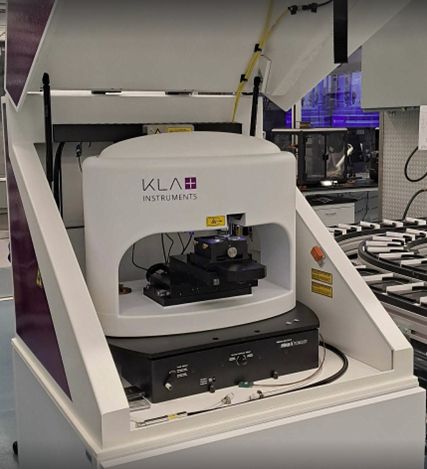
To address these challenges, microstructural characterization in AIMD-L is performed with a unique instrument called MAXIMA (Multimodal Automated X-ray Investigation of Materials). MAXIMA is designed for automated, high-throughput characterization of materials using x-ray diffraction (XRD) and x-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy. It incorporates a liquid metal anode x-ray source with focusing optics to produce a small x-ray spot with sufficiently high energy (24 keV) to make XRD measurements in transmission through samples of structural metals as thick as 1 mm.
With x-ray diffraction we can identify and determine the amounts of crystalline phases present in small regions of our samples as well as the grain size and crystallographic texture. Because the measurements are made in transmission, we measure the microstructure through the entire thickness (in contrast to SEM/EBSD which only examine the surface). A key advantage of transmission XRD for high-throughput work is that no surface preparation is required, dramatically reducing the time required for characterization. With fully robotic sample handling, a small spot size (~200 micron), and a highly sensitive Eiger x-ray detector, MAXIMA is capable of recording hundreds of diffraction patterns per hour.
MAXIMA also provides quantitative information about the chemical composition of specimens by means of x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). This is especially useful for combinatorial specimens where there is a gradient of chemical composition across the sample. XRD and XRF measurements can be made simultaneously, increasing the overall throughput of the system.
Automated data handling and processing is essential for high-throughput characterization. In AIMD-L, data are autonomously streamed from MAXIMA using OpenMSI [link] with automated data analysis pipelines that generate the azimuthally-integrated 1D diffraction patterns and perform quantitative composition analysis from the XRF data. The processed data are immediately available for examination by human operators and for use by the AI/ML algorithms that guide experiments in AIMD-L.